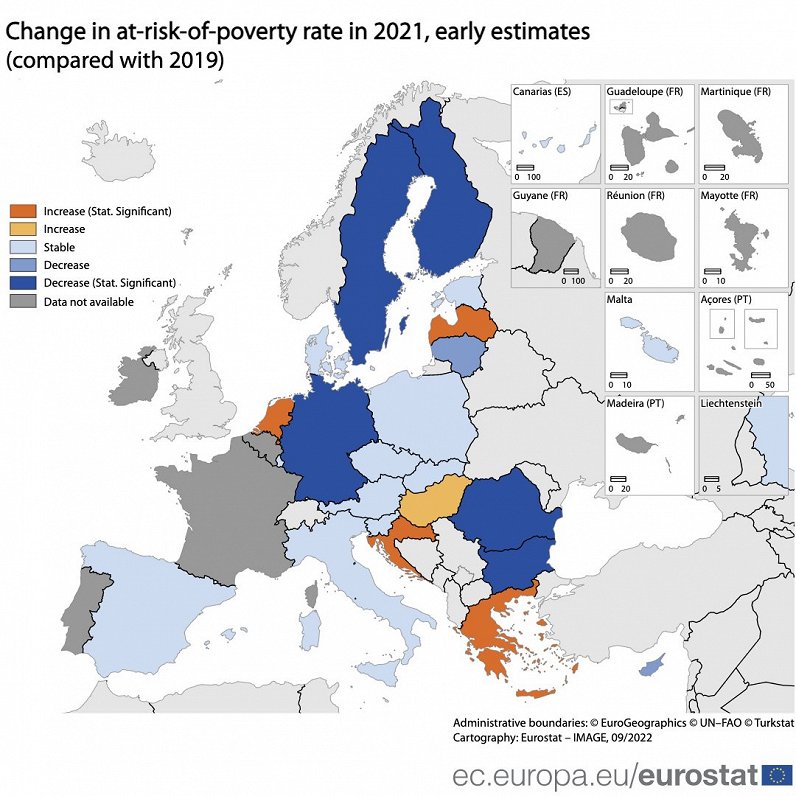
"The at-risk-of-poverty rate in the EU remained stable in 2021, yet the situation varied across the EU Member States, particularly when assessing the cumulated effects," Eurostat said.
"In comparison with the pre-pandemic values of 2019, in 2021, for the Member States with available data, 5 registered an increase in the poverty rate in the 2019-2021 period, of which 4 were statistically significant: Greece, Croatia, Latvia and the Netherlands."
In 11 Member States, the poverty rate was stable, and in the remaining 7, it was estimated to have decreased: Bulgaria, Finland, Cyprus, Germany, Lithuania, Romania and Sweden. The at-risk-of-poverty rate is the share of people with an equivalised disposable income (after social transfer) below the at-risk-of-poverty threshold, which is set at 60 % of the national median equivalised disposable income after social transfers.
💰Early estimates show that for the EU Member States with available data, 5 registered an increase in the at-risk-of-poverty rate in the 2019-2021 period, of which 4 were statistically significant: 🇬🇷Greece, 🇭🇷Croatia, 🇱🇻Latvia and 🇳🇱the Netherlands.
— EU_Eurostat (@EU_Eurostat) September 29, 2022
👉https://t.co/5VkNMwND08 pic.twitter.com/25gcOxRfRF